 Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate
WHAT IS BAKING SODA?
In 1791, the French chemist Nicolas LeBlanc produced sodium carbonate, which is also called ash, for the first time. In 1846, two American bakers, Dujohn Dwight and Austin Church, built the first baking soda factory in America from sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide. Sodium bicarbonate was introduced by Rudyard Kipling in the 1800s; A compound that can be used in commercial trade to prevent spoilage of fresh fish. This application was the most common use of sodium bicarbonate at that time. In 1919, an American senator announced that baking soda could cure the Spanish flu! Some studies at that time showed what baking soda is and what treatment it has for diseases like the flu.
PROPERTIES, CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS
What is baking soda or sodium bicarbonate? Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogen carbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. This compound is a mineral salt that consists of sodium cation (Na+) and bicarbonate anion (HCO3-).
Baking soda is a white solid with a crystalline appearance, but is often sold as a fine-grained powder. Baking soda has a slightly salty taste and is relatively alkaline. The mineral composition containing this salt is found in salt water springs and mineral springs
SODIUM BICARBONATE PRODUCTION METHODS
1- PRODUCTION OF BAKING SODA IN THE INDUSTRY:
In order to better understand what sodium bicarbonate is, it is necessary to get acquainted with the production method of this substance. Sodium bicarbonate is industrially produced from sodium carbonate:
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O →2 NaHCO3
Soda ash, mined as Trona ore, is dissolved in water and treated with carbon dioxide. Sodium bicarbonate is removed from this solution in solid form as a precipitate.
In the case of the Solvay process, sodium bicarbonate is an intermediate compound in the reaction of sodium chloride, ammonia gas, and carbon dioxide. However, this product has a lower purity (75%):
NaCl + CO2 + NH3 + H2O → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
Although it does not have significant commercial and production value, sodium bicarbonate obtained from the reaction of carbon dioxide with sodium hydroxide aqueous solution can also be obtained:
CO2 + NaOH → NaHCO3
2- PRODUCTION OF SODIUM BICARBONATE THROUGH MINING:
Natural deposits of nahcolite contain the mineral composition of sodium bicarbonate. These mines were created in the Eocene period during the formation of the Green River in Colorado. These sediments have gradually settled over time due to the evaporation of the river bed. Commercial extraction of sodium bicarbonate from this area is done using common underground mining techniques such as pit mining, drum drilling and longitudinal mining similar to coal mining. Limited amounts of the product are obtained by extracting sodium bicarbonate solution through pumping hot water from nacolite beds and recovering the dissolved “nacolite” on the surface of the earth. This extraction is done through a crystallization process with natural cooling.
PROPERTIES AND USES OF BAKING SODA
What is sodium bicarbonate? Sodium bicarbonate is an amphoteric compound. Aqueous solutions are relatively alkaline due to the formation of carbonic acid and hydroxide ions. Sodium bicarbonate can be used as a washing agent to remove any acidic impurities from the “crude liquors” and produce a purer sample. The reaction of sodium bicarbonate and acid produces an inorganic salt and carbonic acid, which easily decomposes into carbon dioxide and water:
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2CO3
H2CO3 → H2O + CO2
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acetic acid (found in vinegar) to produce sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide:
NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide to form carbonates: NaHCO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
THERMAL DECOMPOSITION OF SODIUM BICARBONATE
Thermal Decomposition At 80-100°C (176-212°F), sodium bicarbonate gradually decomposes into sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide. The rate of this conversion is faster at 200°C (392°F): sodium bicarbonate NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2 2
On further heating, the carbonate turns into an oxide (above 850°C): Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BAKING SODA
Name of the compound Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Other names: Baking soda - Bicarb - Bicarbonate of soda - Nacolite
Identification indicators
CAS Number 144-55-8
EC Number 8-633-205
E number E500
PubChem CID 516892
Features and properties
chemical formula NaHCO3
Molar mass 84.0066 g mol−1
Appearance White crystals
smell Odorless
density 2.20 g/cm3
melting point Decomposing into sodium carbonate at 50 degrees Celsius
Solubility in water 69 g/L (0 °C)
96 g/L (20 °C)
165 g/L (60 °C)
Solubility in other liquids 0.02 wt% acetone
2.13 wt% methanol at -22 °C
Insoluble in ethanol
structural feature
Crystal structure mono crystal
Thermochemistry
heat capacity (C) 87.6 J/mol K
Molar Entropy (So298) 101.7 J/mol K
Standard enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) -950.8 kJ/mol
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚) -851.0 kJ/mol
Related compounds
Anions Sodium carbonate
cations Ammonium bicarbonate
Potassium bicarbonate
Other similar compounds Sodium bisulfate
Sodium hydrogen phosphate
WHAT ARE THE USES OF BAKING SODA IN INDUSTRY
1- THE USE OF SODIUM BICARBONATE IN THE FOOD INDUSTRY
Sodium bicarbonate is the same as baking soda or sodium hydrogen carbonate. This industrial raw material in food grade is mainly used in the bread and confectionery industries. It can be used as a mixture for preparing dough, boiling in bread dough, buffer environment (= PH adjustment). You can see other items in the following section:
SODIUM BICARBONATE AS A RAW MATERIAL IN THE PREPARATION OF BAKING POWDER:
To increase the volume of the dough, it is necessary to prepare all kinds of bread, sweets, cakes, crackers and wafers, baking powder. Baking powder contains three types of main ingredients:
- A key factor: sodium bicarbonate
- An acidic agent: for example, sodium acid pyrophosphate (SAPP) or citric acid
- A bulking agent: for example, corn starch
The standard ratio is 30/40/30% by weight (starch/sodium acid pyrophosphate/sodium bicarbonate). The action of yeast is accompanied by the release of carbon dioxide. You can see these reactions in the following figures:
Two chemical reactions (reaction 2a and 2b):
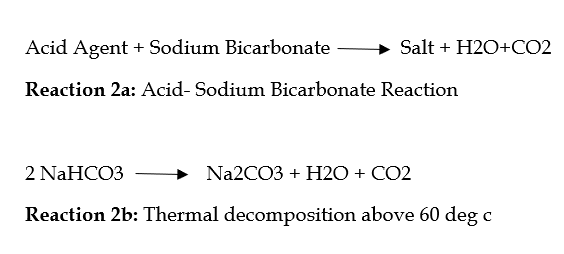 Reaction 2a for carbon dioxide has a higher performance than reaction 2b. Reaction 2a starts when the reagents are dissolved during the preparation of the dough. Reaction 2b starts with heating.
Reaction 2a for carbon dioxide has a higher performance than reaction 2b. Reaction 2a starts when the reagents are dissolved during the preparation of the dough. Reaction 2b starts with heating.
The rate of reaction 2a depends on various parameters, including the choice of acidic material and the size of Baking Soda particles. Sodium bicarbonate with larger particles has a longer dissolution time than smaller particles (see table below), thus affecting the reaction rate. The reaction rate is slower for larger particles than for smaller particles.
However, it should be noted that an adverse reaction may occur if there is too much Baking Soda. (see the reaction in the figure below).
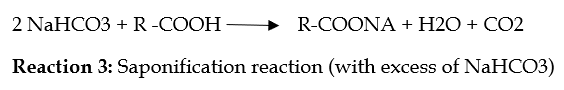 This is a saponification reaction between sodium bicarbonate and free fatty acid in the formulation (fatty acid that comes from ingredients like butter or cream). This reaction produces a fatty acid salt that imparts an unpleasant, metallic taste to cooked ingredients.
This is a saponification reaction between sodium bicarbonate and free fatty acid in the formulation (fatty acid that comes from ingredients like butter or cream). This reaction produces a fatty acid salt that imparts an unpleasant, metallic taste to cooked ingredients.
BAKING SODA AS A PH BUFFER IN THE FOOD INDUSTRY:
Sodium bicarbonate can be used as a pH buffer; This means that it can adjust and maintain the pH of the solution.
With such a feature, some food formulations contain sodium bicarbonate as a pH buffer. All kinds of ready-to-cook noodles, as well as energy drinks and ready-made coffee or tea contain this compound.
In this way, the use of sodium bicarbonate has two main benefits. The first one is the better control of the pH of the final product so that it enables better stability and shelf life of the edible product.
Sodium bicarbonate adjusts the pH and prevents the creation of an acidic environment that causes bacteria to multiply. Second, sodium bicarbonate makes a person feel better during digestion.
SODIUM BICARBONATE CAUSES "FOAM OR GAS" IN FOOD:
The chemical reaction that occurs in the production of foam or foam in the preparation of bread or cake is the same reaction 2a that we mentioned in the previous section. Sodium bicarbonate and an acidic agent react to release carbon dioxide.
This property is used for the formulation of carbonated drinks. As a result of these reactions, carbon dioxide dissolved in soft drinks is released as gas bubbles.
This boiling feature is also used to produce foam in powdered drinks such as cappuccino or powdered energy drinks. This reaction occurs when the powder is mixed with water.
Powdered baking soda has a faster dissolution time in water and produces a strong foam with a quick sparking effect. upside down; Larger particles have a longer dissolution time and a weaker foam is produced.
2- INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS OF SODIUM BICARBONATE
- The human body needs a certain pH range for health. When the acidic nature becomes too much in any of the body systems, sodium bicarbonate ampoule or sodium bicarbonate tablet can quickly counteract the formation of an acid/base reaction by raising the body’s pH. Chronic kidney disease, heartburn, kidney stones, increased uric acid and metabolic acidosis can all be treated with sodium bicarbonate.
- Sodium bicarbonate effectively cleans teeth and gums and reduces the natural acidity of the mouth. If the acidity of the mouth is higher than normal, it can cause oral infections. Therefore, many fluoride-free toothpastes contain sodium bicarbonate.
- 25% of the total amount of baking soda used worldwide is used as a feed additive.
- Industrial grade Baking Soda is used in wool, silk and leather dyeing.
- Baking Soda is used as a purifier and catalyst in the plastic and complex polymer industries. Decomposition of Baking Soda releases carbon dioxide; Significantly, this feature is used in the production of rubber and plastic.
- While cooking peas or other vegetables, Baking Soda is added to make these vegetables softer.
- The mixture of baking soda and olives makes the texture of olives soft and crispy.
- Baking soda is also used in the raw materials of drilling mud.
- Most face stain remover products contain baking soda as a primary ingredient in the formulation.
- Sodium bicarbonate controls the smell of sulfide in sewage treatment plants. It also counteracts the biological growth of microorganisms.
- Due to the increase in pH, the appropriate alkalinity of water is maintained with Baking soda during purification.
- Chemically, Baking soda is used for desulfurization in the exit chimney. This process cleans industrial gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
- The antiseptic property of Baking Soda has made it very valuable in the pharmaceutical industry. This combination kills bacteria and fungi by disinfecting.
- Library managers and book collectors know that by sprinkling Baking Soda on the pages of books, the old smell that is in damaged or older books will disappear.
- Dry chemical fire extinguishers used in homes and businesses contain Baking soda to fight electrical fires.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL AND EDIBLE BAKING SODA
Baking soda is one of the most important chemical compounds used in various industries for various processes. This material has the structure of sodium carbonate, but the situation is slightly different in both industrial and edible grades. By knowing the difference between industrial and edible baking soda, you will find out their most important uses.
In general, industrial baking soda is a combination of sodium carbonate with the formula Na2CO3, which has a lower purity and quality than edible baking soda; Baking soda impurities usually include heavy metals, iron, sodium carbonate, arsenic, and chlorine. But baking soda has higher purity and quality.
This compound is soluble in water and in industrial processes, both materials have carbonate anion and sodium cation. It is widely used in food and medicine. Baking soda is used in the production of carbonated soft drinks and the preparation of dough and cake powder.
Industrial grade baking soda is used for cleaning and removing stains in industries. On the packaging of baking soda, words are written that indicate whether it is food or industrial grade. For edible baking soda, there is the word food grade and for industrial grade, there is the word industrial grade on the bags.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEEN BAKING SODA GRADES
Baking soda is an important compound that is widely used in the food industry, animal feed and industrial applications. This material is used in animal feed with a combination used in the food industry. Both are actually a substance called Baking soda , which is represented by the chemical formula NaHCO3, and both have high quality and purity because livestock and animal feed should be given the same care and attention as humans. In fact, these two grades are not much different! The difference between animal and edible baking soda is in their application. In some cases, edible grade baking soda or Baking soda is used for poultry feed. Which grade of this substance should be used in animal feed does not make much difference, but experts in this field determine this issue according to the health and nutrition status of animals and birds. It may be necessary to add Baking soda to the poultry feed to cure their illness and have more body reserves when laying eggs. The use of industrial, animal and food grade baking soda depends on the type of processes and product or final results. To identify baking soda, you must pay attention to the label on the package. If the word Feed Grade is on the packaging, it indicates that this product is animal feed grade
SAFETY OF SODIUM BICARBONATE
Sodium bicarbonate causes eye and skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. It is likely to be harmful if accidentally swallowed;
- The most important effect is the stimulation of the digestive system.
- Inhalation of dust from this solid compound may cause respiratory tract irritation.
- Chronic damage caused by long-term contact with this mineral includes liver and kidney damage.
CHEMICAL STABILITY OF BAKING SODA
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes when heated. This compound may also decompose when exposed to moist air or water.
- The contact of this material with incompatible materials should be avoided. Dust generation, exposure to excessive heat, temperatures above 50°C (122°F), exposure to moist air or water are incompatible factors for this compound.
- Sodium bicarbonate is incompatible with other substances such as strong oxidizing agents, acids, monoammonium phosphate, sodium and potassium alloys.
- Dangerous decomposition products of this compound include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
STORAGE CONDITIONS FOR SODIUM BICARBONATE
The storage environment for special Baking soda packages and bags should have proper ventilation. Minimize dust generation and accumulation for this material. Try not to let this mixture come into contact with your eyes and skin, and if it accumulates on your clothes, change your clothes immediately and wash them. Sodium bicarbonate packages should be kept in a dry and cool place and the lid of the container should be tightly closed.
BAKING SODA PACKAGING
 Baking soda packaging, sodium bicarbonate packages, in polyethylene or polypropylene bags with a weight of 25 kg and 50 kg with a shrink cover and on a pallet as well as a 1000 kg jumbo bag.
Baking soda packaging, sodium bicarbonate packages, in polyethylene or polypropylene bags with a weight of 25 kg and 50 kg with a shrink cover and on a pallet as well as a 1000 kg jumbo bag.
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET OF SODIUM BICARBONATE
Chemical Formula: NaHCO3
Molecular Weight: 84
Grade: Food/feed Grade
Sodium Bicarbonate Properties
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Odor: Odorless
Melting Point: Decomposes to sodium carbonate starting at 50 °C
Solubility: 9.6 g/ 100ml in water (20° C)
Sodium Bicarbonate Specification
Test Analysis
Purity 99.0 %
As ≤ 3 ppm
Pb ≤ 5 ppm
Iron ≤ 5 ppm
PH Max 8.6
For more information, please Contact our Sales Team.










