 Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
DEFINITION OF CATIONIC BITUMEN EMULSION
The Cationic Bitumen Emulsion is a stable mixture of fine droplets of bitumen dispersed continuously in water by a chemical material called cationic emulsifier. Compared to other bitumen emulsions, cationic bitumen emulsion is more widely used around the world. It is used for surfacing, cold mix asphalt, and road construction. Bitumen emulsion consists of three basic ingredients: bitumen, water, and an emulsifying agent. Based on specifications it may contain other additives, such as stabilizers, coating improvers, anti-strips, or break control agents. It is well known that water and asphalt will not mix, except under carefully controlled conditions using highly specialized equipment and chemical additives.
DECIPHERING THE DYNAMICS OF CATIONIC BITUMEN EMULSION
The term “cationic” derives from the behavior of bitumen particles migrating under an electric field. In this phenomenon, the droplets move towards the cathode (negative electrode), leading to the classification of the emulsion as cationic. The cationic emulsifying agent operates similarly to its anionic counterpart, with the negative portion of the agent’s head dispersing in the water, resulting in a positively charged head. This positive charge is imparted to all the droplets, causing them to repel one another and remain as distinct suspended bitumen drops. A representative cationic emulsifying agent, as well as a diagram illustrating the agent’s orientation at the bitumen-water interface and the positive charge on each droplet, are depicted below. The stable dispersion of bitumen in the continuous water phase is achieved through the presence of positively charged bitumen globules. These globules are enveloped by a cover containing the NH3+ group, providing stability to the emulsion through electrostatic repulsion. These positively charged bitumen droplets possess an affinity for negatively charged aggregates, contributing to their effective bonding. To create this dispersion, bitumen is processed with a water-based solution under controlled conditions using a colloidal mill equipped with a high-speed rotor and carefully selected surfactants/emulsifiers. The choice and quality of the emulsifier play a crucial role in the stability, breaking, and curing of the emulsion when applied over aggregates. In the application of cationic emulsion, positively charged bitumen drops are applied to a negatively charged surface. These bitumen drops are immediately attracted to the surface and initiate the breaking process. Additionally, the emulsion undergoes water loss through evaporation. As a result, cationic emulsion employs two breaking mechanisms simultaneously, leading to faster breaking compared to a corresponding anionic emulsion.
USER BENEFITS OF CATIONIC ASPHALT EMULSION UNVEILED
Cationic asphalt emulsion offers a range of advantages to its users, making it a favorable choice in various applications. Its lower viscosity in comparison to hot-applied bitumen grants it excellent penetration and spreading capabilities, allowing for efficient coverage. One of the significant advantages of bitumen emulsion lies in its inherent electrical charge, which confers built-in antistripping properties. This unique characteristic promotes superior bonding with hydrophilic aggregates commonly found in our country. Consequently, it enhances the overall performance and durability of asphalt surfaces. An additional user benefit is the ability to utilize cationic emulsion even with wet aggregates, enabling construction work to proceed during the monsoon season. This flexibility provides a distinct advantage, allowing for uninterrupted project progress regardless of weather conditions. Unlike conventional bitumen, cationic asphalt emulsion eliminates the need for pre-heating, resulting in a more convenient handling process for users while also leading to cost savings. The absence of pre-heating not only streamlines operations but also contributes to improved safety measures. Energy conservation, pollution control, and safety are critical aspects that cationic emulsion addresses effectively. Over the past decade, the country has actively sought alternatives to hot mixing technology to preserve our environment and reduce reliance on imported petroleum oil and forest-based firewood. Optimal usage of bitumen emulsion contributes significantly to achieving these goals, resulting in multiple benefits:
- Petroleum oil conservation: Bitumen emulsion does not require petroleum solvents or heating to achieve liquidity, thereby saving imported petroleum oil or the need for firewood.
- Reduction of toxic fumes: Traditional heated bitumen and cutbacks emit hydrocarbon fumes, whereas cationic bitumen emulsion eliminates this concern as it does not require heating during application.
- Enhanced safety: Cold application of bitumen emulsion ensures a safer working environment, making it a user-friendly product.
- Accelerated work progress: The ability to apply the emulsion at ambient temperatures facilitates faster project completion, optimizing productivity on-site.
In summary, cationic asphalt emulsion offers a host of user advantages, including improved penetration, effective bonding, monsoon usability, cost savings, energy conservation, pollution control, and enhanced safety measures. Its versatility and positive environmental impact make it a compelling choice for various asphalt applications.
PRODUCTION OF CATIONIC BITUMEN EMULSION
To produce cationic bitumen emulsion, we need pure bitumen, water, and a cationic emulsifier. In general, for the production of cationic emulsion bitumen, it is necessary to dissolve less than 1 %wt of cationic emulsifiers in water. Then, by using a mill which is equipment for producing the cationic bitumen emulsion, the small drops of hot bitumen are separated and mixed well with the solution of water and cationic emulsifier. After that, cationic emulsifiers make fine bitumen drops positive. In addition to the fact that cationic bitumen emulsion is harder to dissolve in water than the anionic type, a series of additives are also needed to make the dissolution process easier.
Cationic Bitumen Emulsions, classified according to their degree of stability from rapid setting to overstabilised systems, with different physical parameters, are made from bitumen from all European and Venezuelan origins for the following applications:
- Bitumen spraying for layer adhesion in hot asphalt construction
- Emulsion-based surface treatment
- Surface treatment using hot binding agent
- Pothole repairs
- Microsurfacing with cold mix
- Joint and crack treatment
- Fleece laying
- Coloured surfaces
Our specialists have years of international experience and can guarantee the perfect quality of the above-mentioned applications thanks to a comprehensive range of modern equipment and machinery.
Additionally, we also offer binding agents and special Bituminous Products:
- Recycling and cement stabilisation emulsions
- Cold mix binding agents as well as cold mix, loose and packaged
- Landscaping emulsions
- Joint bands in all sizes
- Joint sealing compounds, rail joint sealing compounds and under-rail sealing compounds
- The entire spectrum of sealing compounds, bitumen emulsion slurries and repair mortar
- Biodegradable release agents
- Spray can binding agents
- Basement sealing systems
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CATIONIC AND ANIONIC EMULSIONS?
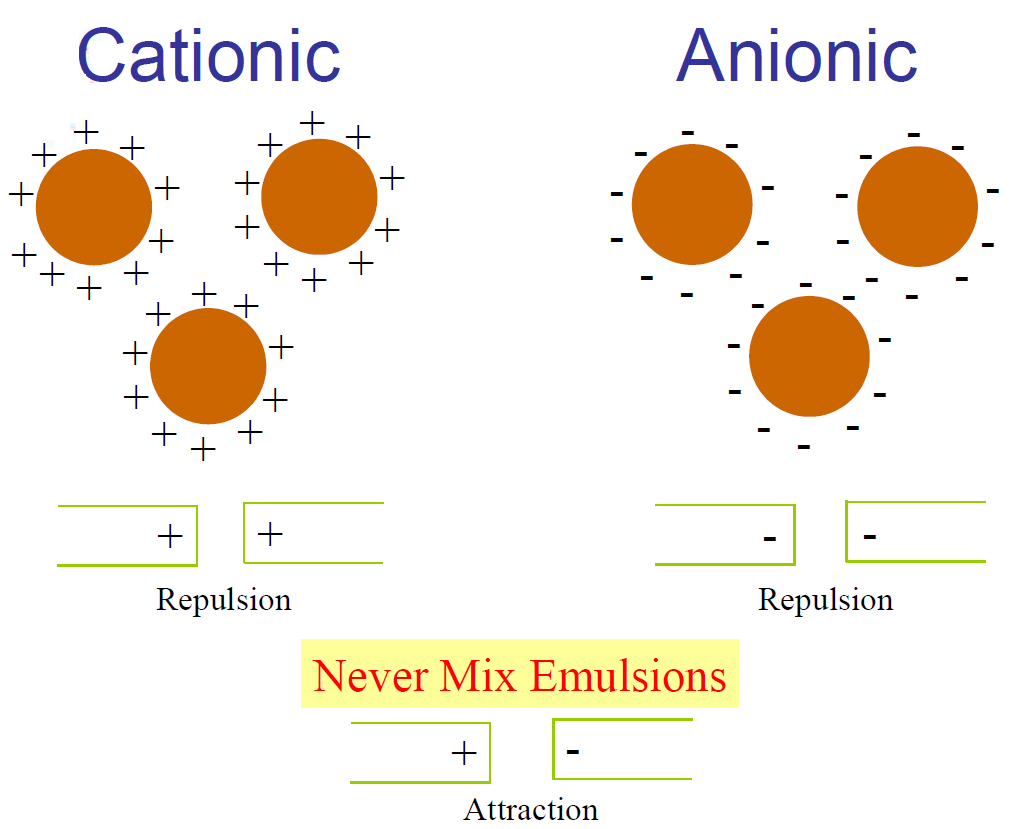 Differences between Cationic and Anionic Emulsions
Differences between Cationic and Anionic Emulsions
There are three main differences between Cationic and Anionic Emulsions. The first and most obvious feature is their charge. The second difference is their solubility in distinct systems. The last distinguishing characteristic is their resistance to certain materials. The manufacturing process of different types of emulsions is distinctive. Thus, not all emulsions are the made the same way. Cationic bitumen emulsions are positively charged while anionic bitumen emulsions are negatively charged. Not only does the surfactant determine the charge of the emulsion, but its choice also impacts the reliability and efficiency of the final product. Moreover, the types of materials that these emulsions dissolve in are also different. Due to their chemical makeup, anionic bitumen emulsions readily dissipate in high pH or alkaline detergents. On the other hand, they have a good resistance to acids. The opposite is true for cationic emulsions, which have a high tolerance for alkaline detergents and are susceptible to dissolving in acid solutions.
- Cationic bitumen emulsions are classified based on setting time.
- An emulsion’s setting time is a measure of how fast dispersed bitumen drops are joined together and settle on the paving surface.
- In other words, after applying bitumen emulsion to the surface, the setting time showed how long it takes for bitumen and water to separate from each other.
CLASSIFICATION FOR CATIONIC EMULSION INCLUDE:
This type of bitumen emulsion breaks as soon as it is applied on any surface.
This type of bitumen emulsion is used in road constructions that have medium grain sizes. After applying MS cationic emulsion bitumen on the surface, it will break only if dust and small particles of air enter it. Otherwise, its water should evaporate. Then it can play the role of bitumen and bind the grains.
- Bitumen emulsions of this type have a slow setting time. Bitumen setting time in this type only depends on the water evaporation rate.
- It is used on aggregates that are very fine.
- This type of bitumen can penetrate into very small pores without breaking.
THE BELOW TABLE SHOWS DIFFERENT TYPES OF CATIONIC BITUMEN EMULSION
CRS CMS CSS
CRS-1 CMS-1 CSS-1
CRS-1h CMS-2 CSS-2
CRS-2 CMS-1h CSS-1h
CRS-2h CMS-2h CSS-2h
For more information, please Contact our Sales Team.

